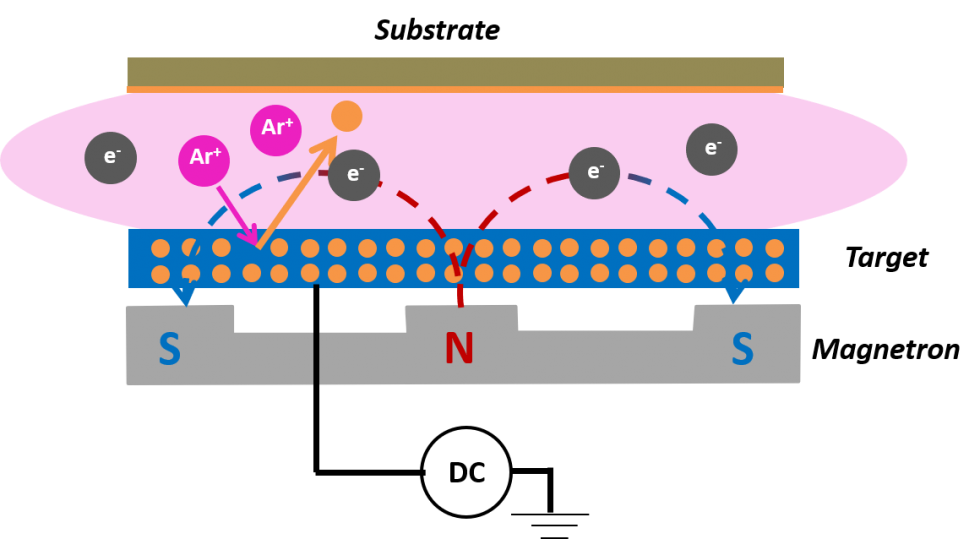
Sputtering targets are materials used for thin film deposition. Sputtering technology is used to sputter material atoms or molecules from solid targets and then form thin films on substrates. Sputtering targets are widely used in the electronics and information industries, including semiconductor chips, solar cells, flat panel displays, information storage and other fields.
Sputtering target process flow
Raw material powder–powder smelting–powder mixing–pressing molding–atmosphere sintering–plastic processing–heat treatment–ultrasonic flaw detection–water cutting–machining–metallization–binding–ultrasonic testing–ultrasonic cleaning–inspection–shipping.
Among them, the specific meanings of the main processes are as follows:
Powder smelting: the raw material powder is subjected to preliminary atmosphere sintering to control the gas content in the raw material powder.
Powder mixing: the target material has a unique formula, and the content of each component needs to be accurately controlled, and the impurity content needs to be strictly limited. In the process of powder metallurgy, it is necessary to fully mix the elements evenly, and the particle size distribution is uniform to prevent pollution, and a mixed composite powder needs to be prepared by special process means.
Pressing molding: the target material prepared by powder metallurgy process needs to pre-press the powder material to make it a medium-density green body. Its density uniformity and internal defects affect the yield of high-temperature sintering in the later stage.
Atmosphere sintering: The pre-pressed green body needs to undergo one or more high-temperature sintering. Different sintering temperature curves are selected according to different materials, and different sintering environments, such as sintering atmosphere and sintering pressure, are selected to prepare high-density target blanks.
Plastic processing: The metal billet needs to undergo a large plastic deformation to obtain sufficient length, width and thickness dimensions, and to allow the internal grains to undergo sufficient tensile deformation, thereby generating enough dislocations inside. Heat treatment: After the metal billet undergoes a large plastic deformation, the heat treatment process is selected according to the characteristics of different materials, so that the metal material can be recrystallized and the internal stress of the material can be removed.
Ultrasonic flaw detection: After the target blank is processed, ultrasonic waves need to be used to check whether there are defects inside the material. After the target blank is bonded to the back plate, a water-immersion ultrasonic scanner needs to be used to detect the bonding layer to check whether the bonding area meets the standard.
Mechanical processing: The target blank needs to be processed by precise mechanical forming. The back plate used in combination with the target blank needs to have extremely high dimensional accuracy and mechanical strength due to its precise coordination with the coating equipment and high-pressure water cooling. The processing difficulty is relatively high, especially for the back plate with an internal circulation water channel. Due to the particularity of the material, the closed welding of the water channel is very difficult and requires a special welding process.
Metallization: Before the target blank and the back plate are bound, in order to enhance the metal wetting properties of the target material and the target material and the solder, the welding surface needs to be pre-treated so that a transition layer is plated on the surface.
Bonding: Most target materials cannot be directly installed for coating due to the physical or chemical properties of the material. Metal solder is needed to weld the target blank and the back plate together, and the effective bonding rate of the surface needs to reach a large area welding greater than 95%. The whole process needs to be carried out under high temperature and high pressure.

SPUTTERING TARGET - MANUFACTURING PROCESS
The manufacturing process of targets commences with a unique process design, tailored to the performance and requirements of the intended downstream application. This process involves repeated plastic deformation and heat treatment, followed by mechanical processing, cleaning, drying, and vacuum packaging.
The predominant preparation methods for sputtering targets currently include the casting process and powder metallurgy process.
| Preparation Process | General Type | Features |
|---|---|---|
| Smelting and casting process | Vacuum induction melting Vacuum arc melting Vacuum electron bombardment smelting |
Compared to the powder method, the alloy targets produced through smelting exhibit lower impurity content, particularly in terms of gas impurities, and are characterized by high energy and density. However, for alloys comprising metals with significant disparities in melting points and densities, achieving uniform composition in smelted alloy targets is generally challenging. |
| powder metallurgy process | Hot pressing Vacuum hot pressing Hot isostatic pressure (HIP) |
Obtaining a uniform, fine-grained structure is facilitated by this method, which also conserves raw materials and enhances production efficiency. The critical factors include: selecting high-purity, ultra-fine powder as the raw material; employing forming and sintering technologies capable of rapid densification to ensure the target’s low porosity and control the crystallization particle size; and rigorously controlling the introduction of impurity elements during the preparation process. |
| Extrusion process | Hot extrusion Cold extrusion Warm extrusion |
Mainly used to prepare metal and alloy rotating targets with good plasticity such as aluminum-copper-zinc-nickel-chromium alloy. |
| Plasma spraying process | vacuum Water stability Gas stability Plasma spraying |
Mainly used to prepare brittle metal and alloy ceramic targets, such as metal chromium, silicon, silicon aluminum alloy, oxide and other rotating targets. |
VI HALBLEITERMATERIAL GmbH offers an extensive range of high-purity, high-performance sputtering target materials, available in various shapes and compositions. Our inventory includes circular sputtering target, rectangular sputtering target, triangular sputtering target, planarsputtering target, rotary sputtering target, and ring sputtering targets, with purities ranging from 99.0% to 99.9999%.
Custom fabrication of most sputtering targets to any shape and size, based on provided drawings, is feasible. For sputtering targets with technical constraints on the maximum size of a single piece, segments can be joined using butt or angled joints to form a multi-segment sputtering target.
Should the required sputtering target materials/specifications not be listed, we encourage you to contact us.
What we can provide?
| Metal | Alloy | Oxide | Ceramic (Non-Oxide) | Chalcogenide | Precious Metal | Rare Earth | Halide | Compound |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Al | AlCo | Al₂O₃ | AlN | Bi₂Te₃ | Ag | Ce | CsI | ATO |
| Ba | AlCr | AlON | B₄C | BiSbTe | AgCr | CeGd | InF₃ | AZO |
| Bi | AlCu | CdO | BN | BiSbSe | AgCu | CeSm | LiF | FTO |
| Co | AlMg | Cu₂O | Cr₂AlC | CdS | Au | Er | MgF₂ | IGZO |
| Cu | AlNi | Fe₃O₄ | CrSi₂ | FeS | Ir | Gd | PbCl₂ | ITO |
| Fe | AlSi | Ga₂O₃ | GaN | GeS₂ | IrMn | La | YbF₃ | IZO |
| Ge | CoCr | HfO₂ | MgSi₂ | MoS₂ | Pd | La₂O₃ | KF | YSZ |
| Hf | CrNb | In₂O₃ | Mo₂C | MoSe₂ | PdAg | La₂Zr₂O₇ | ZnF₂ | ZTO |
| In | CrSiAl | Li₂O | MoSi₂ | NbSe₂ | PdNi | LaB₆ | MoCl₅ | BaTiO₃ |
| Li | CuSn | MoO₃ | NbN | SnS₂ | Pt | Sm | NbCl₅ | BaVO₃ |
| Mg | CuZn | Nb₂O₅ | Si₃N₄ | ZnS | Rh | SmB₆ | ZrF₄ | BiFeO₃ |
| Mn | FeCrAl | NiO | SiC | CdTe | Ru | SmCo | … | BiVO₄ |
| Mo | MoNb | Sb₂O₅ | TaC | ZnSe | … | Tm | KNbO₃ | |
| Nb | MoTa | SiO | TaN | ZnTe | Y | Li₃PO₄ | ||
| Ni | MoW | SiO₂ | Ti₃SiC₂ | CaSe | Yb | LiCoPO₄ | ||
| Sb | NbTi | SnO₂ | TiB₂ | FeSe | Yb₂O₃ | LiSiO₄ | ||
| Sc | NbZr | Ta₂O₅ | TiN | Cu₂Te | YBCO | LiFePO₄ | ||
| Se | NiAl | TiOx | VN | CuTe | YPO₄ | MgTiO₃ | ||
| Si | NiCr | V₂O₅ | VSi₂ | NiTe | … | MgSiO₃ | ||
| Sn | NiFe | ZnO | WC | MoTe₂ | SrTiO₃ | |||
| Ta | NiSi | ZrO₂ | WSi₂ | … | SrNbO₃ | |||
| Te | NiV | … | ZrB₂ | ZnTiO₃ | ||||
| Ti | SiFe | ZrC | ZrNbO₃ | |||||
| V | TiAlSi | … | … | |||||
| W | TiZr | |||||||
| Zn | WRe | |||||||
| Zr | WTi | |||||||
| … | ZnSn | |||||||
| … |
