Boron nitride is a crystal composed of nitrogen and boron atoms, with the molecular formula BN, molecular weight 24.81, chemical composition 43.6% boron and 56.4% nitrogen, theoretical density 2.27g/cm3.
Boron nitride powder has the properties of loose, lubrication, light weight, easy to absorb moisture, etc., and the colour is white. Boron nitride products are ivory white.

Boron nitride was first discovered in Bellman’s laboratory more than 100 years ago, and the material was developed on a large scale in the late 1950s.
Boron nitride (BN) is a new type of ceramic material with excellent performance and great development potential. It includes 5 isomers, namely hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), wurtzite boron nitride (w-BN), rhombic boron nitride (r-BN), cubic boron nitride (c-BN) and orthorhombic boron nitride (o-BN). At present, the research on boron nitride mainly focuses on its hexagonal phase (H-BN) and cubic phase (C-BN).
The properties of boron nitride can be mainly divided into the following aspects:
✔In terms of mechanical properties: it has the advantages of non-abrasiveness, low wear, dimensional safety, good lubricity, fire resistance and easy processing.
✔In terms of electrical properties: it has the advantages of good dielectric strength, low dielectric constant, low loss at high frequency, microwave penetration, good electrical insulation, etc.
✔In terms of thermal properties: it has the advantages of high thermal conductivity, high heat capacity, low thermal expansion, thermal shock resistance, high temperature lubricity and high temperature stability.
✔In terms of chemical properties: it has the advantages of non-toxicity, chemical stability, corrosion resistance, oxidation resistance, low moisture, biological stability and non-stick properties.
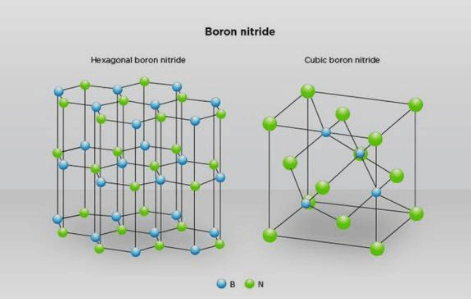
Hexagonal Boron Nitride
Hexagonal Boron Nitride (h-BN) is the most commonly used form of boron nitride. The structure of h-BN is similar to that of graphite, with a hexagonal layered structure, lattice constants a=0.2504nm, c=0.6661nm, theoretical density 2.27g/cm3, melting point 3000℃, soft texture, strong processability, and white color, commonly known as “white graphite”.
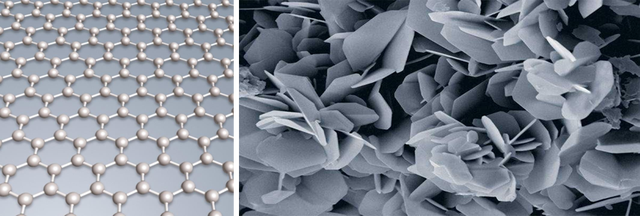
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) has excellent electrical insulation, excellent chemical stability and excellent dielectric properties.
Thermal properties of hexagonal boron nitride: no obvious melting point, sublimation at 3000℃ in 0.1MPA nitrogen, melting point 3000℃ in inert gas, heat resistance to 2000℃ in neutral reducing atmosphere, use temperature up to 2800℃ in nitrogen and argon, poor stability in oxygen atmosphere, use temperature below 1000℃.
Hexagonal boron nitride is one of the thermally conductive materials in ceramic materials, with a thermal conductivity ten times that of quartz, and a higher thermal conductivity of 60W/(m·K) in the direction perpendicular to the c-axis;
Low thermal expansion coefficient, equivalent to quartz, is the smallest among ceramics, with a thermal expansion coefficient of 41*10-6m/K in the c-axis direction and 2.3*10-6m/K in the d-axis direction, so it has good thermal shock resistance.
Mechanical properties of hexagonal boron nitride: The friction coefficient is as low as 0.16, and it does not increase at high temperatures. It has higher temperature resistance than molybdenum disulfide and graphite. It can be used up to 900℃ in an oxidizing atmosphere and up to 2000℃ in a vacuum. The lubrication performance is poor at room temperature, so it is often mixed with graphite fluoride, graphite and molybdenum disulfide as a high-temperature lubricant.
Hexagonal boron nitride is a soft material with a Mohs hardness of only 2. It has good machinability and can be turned, milled, planed, drilled, ground and cut with high machining accuracy, so it can be processed into high-precision parts and products by general mechanical processing methods.
Electrical properties of hexagonal boron nitride: Hexagonal boron nitride is a good conductor of heat and a typical electrical insulator. The room-temperature conductivity can reach 10^16~10^18Ω/cm, and even at 1000℃, the resistivity is still 1014~106Ω/cm. The dielectric constant of h-BN is 3~5. The dielectric loss is (2~8)*10-4, and the breakdown strength is twice that of Al2O3, reaching 30~40kV/mm, so it is an ideal high-frequency insulation, high-voltage insulation, and high-temperature insulation material.
Chemical properties of hexagonal boron nitride: HBN has excellent chemical stability. It does not react with general metals, rare earth metals, precious metals, semiconductor materials, glass, molten salts, inorganic acids, and alkalis. It neither wets nor acts on most metal melts, such as steel, stainless steel, Al, Fe, Ge, Cu, Ni, Zn, etc. Therefore, it can be used as a high-temperature thermocouple protective cover, a crucible for molten metal, a vessel for conveying liquid metal, a pipe for conveying liquid metal, pump parts, a mold for cast steel, and a high-temperature electrical insulation material.
Cubic Boron Nitride
Cubic boron nitride (c-BN) was first synthesized by General Electric (GE) in the United States in the 1950s under high temperature and high pressure conditions. Its hardness is second only to diamond and far higher than other materials, so it and diamond are collectively called superhard materials.
Superhard materials are widely used in sawing tools, grinding tools, drilling tools and cutting tools. Diamond is easily oxidized at high temperatures, especially with iron elements, and is not suitable for iron-based ferrous metal processing. Cubic boron nitride has a crystal structure similar to diamond, and its hardness is slightly lower than diamond. It is often used as abrasive and tool materials.
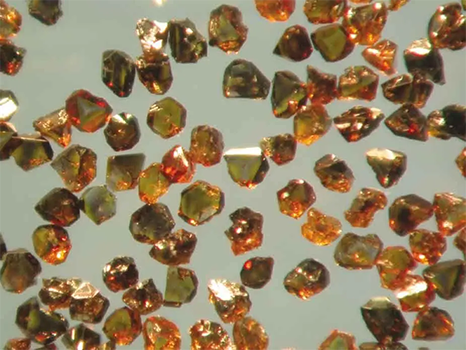
In 1957, R.H. Wintoff of the United States first developed cubic boron nitride, but natural cubic boron nitride has not been found so far.
The properties of cubic boron nitride mainly include high hardness and thermal stability, and its microhardness is second only to artificial diamond.
✔ Its thermal stability is better than that of artificial diamond, and it can still maintain sufficiently high mechanical properties and hardness at high temperatures, and has good red hardness;
✔ It has a stable structure, high oxidation resistance, good chemical stability, especially better than diamond, and does not react chemically with iron group elements at temperatures as high as 1100~1300℃, so it is particularly suitable for processing ferrous metal materials;
✔ The thermal conductivity is smaller than that of diamond, but higher than that of cemented carbide, and has good thermal conductivity;
✔ High bending strength;
✔ As a grinding tool material, it has a long service life and good wear resistance.
However, single crystal cubic boron nitride has a small grain size, anisotropy, and a cleavage plane that is easy to split. It is brittle and very easy to be cleaved.
c-BN has high hardness, chemical inertness and thermal stability at high temperatures, so it is widely used as an abrasive c-BN grinding wheel in grinding processing.
Because c-BN has characteristics superior to other tool materials, people have tried to apply it to cutting processing from the beginning, but the particles of single crystal c-BN are small and it is difficult to make tools, and the sintering property of c-BN is very poor, making it difficult to make larger c-BN sintered bodies. It was not until the 1970s that the former Soviet Union, China, the United States, the United Kingdom and other countries successfully developed c-BN sintered bodies as cutting tools – polycrystalline cubic boron nitride PCBN. Since then, PCBN has been used in various fields of cutting processing with its superior cutting performance, especially in the cutting processing of high-hardness materials and difficult-to-process materials.
What's the application fields of boron nitride?
Boron nitride is a highly efficient thermal conductive filler with excellent thermal conductivity, insulation performance and chemical stability. It is widely used in high-temperature, high-pressure, high-speed and high-precision thermal conductive fields, such as electronic devices, aerospace, new energy vehicles, chemical equipment and other industries with high heat dissipation requirements.
In the field of electronic devices, it can be used as materials such as thermal conductive plates, thermal conductive pastes, thermal conductive gels, radiators, etc., to effectively reduce the temperature of electronic devices. It can be used in consumer smart device terminals such as smart phones, smart watches, laptops, drones, etc. to stabilize their performance and increase their service life.
In the field of aerospace, it can be used to manufacture high-temperature structural materials, thermal conductive materials, thermal barrier coatings, etc., and used in satellites, detectors, space stations, etc. to improve the performance and safety of aerospace vehicles.
In the field of new energy vehicles, it can meet the heat dissipation requirements of automotive systems such as motors, electronic controls, and batteries, and improve the performance and economy of automobiles.
In the field of chemical equipment, it can manufacture high-temperature reactors, catalysts, and heat transfer equipment to improve the efficiency and safety of chemical equipment.
